Direct Brain-to-Brain Communication – the Basis for Reiki, Chi Healing and “Laying on Hands”. Todd Murphy, 2021

Summary:
Chi (“Qi” or “Ki” in Japanese, as in “Aikido” or “Reiki”) is the “subtle energy” or “life force” that’s the foundation for acupuncture, some martial arts, and traditional Asian healing “by laying on hands”. In Chinese tradition, Chi doesn’t have a physical basis. However, there is evidence that suggests it may be a magnetic phenomenon. Whether it’s physical or not depends on your definition for the word ‘matter’.
Chi or Reiki (another name for Chi) practice can create magnetic fields in the practitioner’s hands, and magnetic fields can pass information between brains. Reiki also appears to synchronize some of the activity between the brains of the practitioner and the brains of their clients.
Spiritual healing may work by passing information from the healer’s brain to the client’s brain through magnetism that runs through the healer’s hands, recruiting local neurons in the area where the area where they apply them. brain-to-brain communication also happens directly between brains in other contexts.
Whether it’s called “healing by laying on hands”, “spiritual healing”, “energy healing”, “Qigong” or even “quantum healing” (a misnomer). This ancient technique is found everywhere in the world, and seen throughout history.
However, healing hands may actually be healing brains, and the healing force may be the force of magnetism, carrying the message from the healer’s brain to the patient’s brain and from there to their body: “be thou healed and made whole.”

Spirituality & The Brain (Home Page)
We’re going to look at a somewhat strange and unexpected scientific discovery. It appears that some Chi healers and Chi workers can emit “extraordinary large” magnetic fields from their hands. These are people who deal with “subtle energies” or as they’re known in China (where they’re a lot less “woo-woo” than they are here in the West), “Chi Kung Healers”. The study was published in 1992, but appears to have escaped the notice of most consciousness researchers and writers in the field.
Seto, Akira, Chikaaki Kusaka, Seiki Nakazato, Takao Sato, Tadashi Hisamitsu, and Chifuyu Takeshige. “Detection of extraordinary large bio-magnetic field strength from human hand during external Qi emission.” Acupuncture & electro-therapeutics research 17, no. 2 (1992): 75-94.
It looks like some “energy healers” emit or manifest strong magnetic fields from their hands. In this case, the scientists worked with “Chi” healers, acupuncturists, some Zen and yoga practitioners, as well as people doing traditional Asian health exercises (e.g. Tai Chi). Of course, none of this applies to frauds or charlatans.
The study was carried out by several scientists in Japan (Seto, et al.), who measured magnetism from the hands of 37 experienced Chi workers, three of whom exhibited strong “biomagnetic fields”. These had a field strength of approximately two to four milligauss (mG), in the frequency range of four to ten hertz. That’s a very low frequency, and it includes the “theta range”, associated with dream imagery, trance, imagination, and memory. The magnetic fields measured from these Chi Master’s hands were a thousand times stronger than the normal field strengths we find in humans. For comparison, old-fashioned (cathode ray) televisions have field strengths of about 3.5 mG, at a distance of 1 to 2 meters. Hairdryers have 12 mG, and stereo headphones, have field strengths running from zero to 100 mG (depending on the volume).
One of the three subjects with strong magnetic fields was measured to see if there was a corresponding electric current, because there are clear laws of physics that tell us that wherever there’s a magnetic field, we can expect to find corresponding electrical activity. In this case, it did not appear. That’s a very significant anomaly, one that might eventually help us to understand consciousness or the many phenomena that contribute to it. As I have suggested in other places, I believe that consciousness (defined as the capacity for subjective experience) is probably going to turn out to be an intrinsic property of magnetic fields, and magnetic fields without corresponding electrical activity may well mean that biological evolution has found a way to sidestep the normal laws of physics. Many anomalous human experiences and aspects of consciousness may actually be magnetic phenomena. Perhaps one day “woo-woo” will be replaced by “whoa!” In fact, Dr. Michael Persinger and others have looked into this very field for decades, and found associations between magnetic activity and direct brain-to-brain communication, psychic perception, remote viewing and a range of other phenomena that many researchers feel are 1) legitimate, and 2) within the domain of consciousness research.
DEBATE ( Sorry. Just one page of it.)
About twenty years later, another group of researchers decided to look into Seto’s experiment again. They published what they said was a repeat of some experiments, including the one we just discussed, to see whether or not they could detect magnetic fields from the hands or body of Chi practitioners. They did not succeed.
Baldwin, A.L., Rand, W.L. and Schwartz, G.E., 2013. “Practicing Reiki does not appear to routinely produce high-intensity electromagnetic fields from the heart or hands of Reiki practitioners“. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 19(6), pp.518-526.
There was a problem with their supposed replication. While the original experiment used 37 subjects, and found three of them demonstrated this very high magnetic field, Baldwin (et al.) only used three subjects who had any experience with Reiki. Only about eight percent of Seto’s original subjects (all experienced Chi Practitioners) demonstrated these strong magnetic fields.
Baldwin (et al.) only worked with three Reiki masters (as they called them in their study) and as a result, even if they had the same percent of subjects producing these very strong magnetic fields, it still might have never shown up in their data.
Seto’s subjects had to satisfy three conditions: 1) they had to make the claim that they could emit “external Chi” as he called it. 2) They had to have other people who were willing to vouch for their abilities and 3) they had to be ordinary healthy people. No such criteria were applied in the so-called repeat of Seto’s experiment.
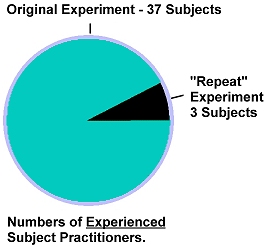
Here’s a pie chart showing the number of subjects in the purported replication, compared with the number of subjects in the original study. As you can see, the so-called “repeat” of the experiment simply wasn’t one. They would have needed a much larger number of subjects for the same effect to appear. Seto measured it in about one out of 12 Chi practitioners. Baldwin didn’t even have 12, they only had 3, and that’s not enough to expect the strong magnetic field to appear in even one subject.
For the last 10 years or so, we’ve been hearing about a thing called the “replication crisis” especially in behavioral and psychological studies, where replications aren’t able to get the same results as the original experiments. This difference in the number of subjects between the Seto procedure and the Baldwin procedure; between the original study and the so-called repetition, makes me wonder how many of the failed replication studies actually replicate the original conditions, the original procedures, or the original subject pool (“cohort”) of the first study.
As I’ve looked at replication studies, I’ve noticed that many researchers are willing to cut corners when they’re doing them, especially if they’re skeptical about the initial result. If they’re skeptical, they may want to see it fail, and by setting up their experiments with different standards than were applied in the original studies, they’re able to arrange for just that.
FURTHER STUDIES
Let’s have a look at another study to do with Reiki and Chi. If we can assume that there’s a reason that Reiki or Chi Healing has a strong and very positive reputation in Asia, we have to wonder how the healing is accomplished. Is there something being “transmitted” between the practitioner and their client? The Seto study makes it easy to accept that there is, and that whatever it is, magnetic fields are its most likely carrier or “medium”.
There is one way we can be sure that Reiki or Chi being transmits something (or that some information is being shared), but it involves more than just looking at how effective Reiki is. There are many studies examining the efficacy or the effectiveness of Reiki are limited by the fact that subjects only received one session, and that’s not how Reiki is usually practiced), but what we’re looking at here is how Reiki actually works, and there is a study gives us an important hint. It showed that brain activity shared between the practitioner and the client was greater during the Reiki session than without it. This was limited to the theta range (included in the frequencies that Seto found in the magnetic fields from the hands of his three subjects with strong magnetic fields), and only over the left hemisphere of the brain.
Ventura, A.C. and Persinger, M.A., 2014. Enhanced coherence within the theta band between pairs of brains engaging in experienced versus naïve Reiki procedures. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 20(8), pp.649-653.
It looks as if there’s something like an information-bearing magnetic ‘conduit’ connecting the practitioner and the patient, one that only affects a certain part of their brains. Only the theta band, in just one area of the brain, may not sound like very much. Some people might think: ‘well, why don’t their whole brains become more coherent’? The answer is: probably because the brain uses energy efficiently, and it just doesn’t need more than that to elicit a response. It may be that only a little bit of electrical or magnetic activity is affected in this process, but that may not have any bearing on the outcome. The common belief that a ‘balanced’ brain or using the ‘whole’ brain is better actually doesn’t have any support from modern neuroscience. More is not better.
You can take a tiny little (itty-bitty) remote control, connect it to an electric steam shovel and use a minuscule amount of energy to tell it to turn on, but it can use an enormous amount of power once it’s running.
This metaphor allows us to see how tiny changes in the brains of people doing Reiki might actually be able to affect changes in someone else’s brain activity. Here is a layout of the differences in coherency; again, in the theta band again over the left hemisphere, with subjects and controls. The solid line shows the degree of coherency with Reiki, and the broken line shows the degree of coherency with only the “sham”, control subjects or as they’re called in this paper, the “naive subjects ;” subjects who had never experienced Reiki before.
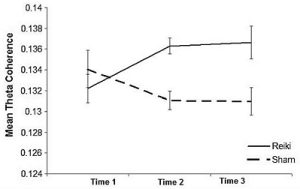
We can see that there’s a significant difference. It’s not huge, but the brain doesn’t need an enormous difference in power, or an enormous amount of power, to make a change in someone’s state of consciousness. Again, think of our remote that turns on a steam shovel, which can then lift many tons at once, beginning with a command that might use only tiny amounts of electricity. A change in state can be triggered by a faint command from a very small brain area, but it can still elicit a whole-brain response. We have to wonder what information is in these direct connections between two brains. There are a few studies that offer us some clues, from a new field that studies “brain–to–brain” communication. The content of brain-to-brain communication may mostly be emotional. In most, but not all, of the studies we’ll be looking at next, the content of the ‘interbrain’ information seems to be more about feelings than thoughts, or depend on emotional bonds.
Supporting Research.
In one such study, published in the “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences”, (an extremely prestigious scientific journal) we find that there is brain-to-brain coupling in the 8 to 12 hertz range (overlapping with theta activity) when a person who’s in pain is holding hands with someone who’s there to support them.
Goldstein, P., Weissman-Fogel, I., Dumas, G. and Shamay-Tsoory, S.G., 2018. Brain-to-brain coupling during handholding is associated with pain reduction. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences, 115(11), pp.E2528-E2537.
These findings suggest that this brain-to-brain coupling may be due to the direct exchange or sharing of information between their two brains, outside of any known mechanism for transmitting information. To put it a little bit crudely, we’re talking about telepathy here, even though that’s a word that invites ridicule. A lot of scientific journals don’t like to publish articles about it, and many scientists don’t like to use it anymore (“spooky action at a distance”). Now, we hear about “brain-to-brain” communication. One reason for that is that while brain-to-brain communication could reflect direct transmission of magnetic signals from one person to another, some may be the result of activity in mirror neurons. (Mirror neurons are a kind of neuron that respond, both when an individual executes a specific motor act and also when they observe another individual performing the same or similar act). It clearly doesn’t apply in some of the cases we’ll look at, because we see the same, yoked, neural patterns elicited by different behaviors, like talking and listening.
The hypothesis we’re looking at here is that extremely weak magnetic fields may be one way information is transmitted from one brain to another. It may rely on the 5 million magnetite crystals per gram in the human brain.
Hosseini, E., 2021. Brain-to-brain communication: the possible role of brain electromagnetic fields (As a Potential Hypothesis). Heliyon, 7(3), p.e06363.
Faint magnetic fields can bear information, and magnetic signals can pass through all structures in the head without any significant attenuation and/or loss of information. Remember that there’s an intimate relationship between electrical activity and magnetic fields. Wherever there’s an electric current or an electric pulse, there will be a corresponding magnetic field or burst of magnetism. This means that the brain’s magnetic fields, whose strength (on a small scale) rises and falls in sync with nearby electrical activity, are one way the information content of that electrical activity, (encoded in pulses, bursts, spikes, etc) can be carried from one person to another. Nothing can block a magnetic field – it’s against the laws of physics.
An astute reader might wonder is whether or not this kind of information sharing between human brains is limited to healing processes, or does it also come up in more unpleasant circumstances? And the answer is yes, it does.
Let’s have a quick look at a study on that very subject.
The title of the article is “Suffer together: Bond Together: Brain-to-Brain synchronization and Mutual Affective Empathy (that means “emotional empathy”) When Sharing Painful Experiences.”
Peng, W., Lou, W., Huang, X., Ye, Q., Tong, R.K.Y. and Cui, F., 2021. Suffer together, bond together: brain-to-brain synchronization and mutual affective empathy when sharing painful experiences. NeuroImage, p.118249.
This study, which used EEG to monitor pairs of people, one of whom was expecting some kind of pain, while the other wasn’t, found that expecting high intensity pain induced greater brain-to-brain synchronization than expecting milder pain. It goes on to say that these results support the hypothesis that sharing a painful experience triggers emotional resonance through brain-to-brain synchronization, and motivates “pro-social behavior within pairs of individuals”. In other words, brain-to-brain synchronization appears when pairs of individuals are relating to one another, and helps us to get along together. It also gives some truth to words of comfort that have stood the test of time: “I feel your pain.”
Sympathy and empathy aren’t just a good idea. They are also part of our primary evolutionary strategy, which consists of relying on other people through a shared, complex, culture.
There are many other circumstances in which human brains can also communicate directly, become partly “locked” together, or partially synchronized with one another.
In one case, the brains of 12 pairs of guitarists playing together synchronized and seemed to share more activity between them when they were playing than when they weren’t. Interestingly, the more difficult the composition, the more the guitarist’s brains locked together, especially in two bands of brain activity (delta and theta).
Sänger, J., Müller, V. and Lindenberger, U., 2012. Intra-and interbrain synchronization and network properties when playing guitar in duets. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 6, p.312
A very similar effect was also found with singing. When people sing together, Their left inferior frontal lobes synchronize or link up with one another.
Osaka, N., Minamoto, T., Yaoi, K., Azuma, M., Shimada, Y.M. and Osaka, M., 2015. How two brains make one synchronized mind in the inferior frontal cortex: fNIRS-based hyperscanning during cooperative singing. Frontiers in psychology, 6, p.1811.
Another study involved pilots and co-pilots, who showed “dense patterns of connectivity” when they were working together, but not when they weren’t actively cooperating or working on the same job.
Toppi, J., Borghini, G., Petti, M., He, E.J., De Giusti, V., He, B., Astolfi, L. and Babiloni, F., 2016. Investigating cooperative behavior in ecological settings: an EEG hyperscanning study. PloS one, 11(4), p.e0154236.
Pairs of brains tend to synchronize their activity when one person tells a story to another, and the researchers who made this discovery suggested that this brain entrainment wasn’t merely a side effect or “epiphenomena” associated with “auditory processing”. To me, it seems to be part of our communication style and strategy, a recondite feature of our ways of relating to one another, and that makes it a part of the human sense of self. A part of who we are, and we are social species, for whom “no man is an island”. The evolutionary path we’ve followed would resoundingly amplify any enhancement in our ability to relate to other and increase our social bonds.
Pérez, A., Carreiras, M. and Duñabeitia, J.A., 2017. Brain-to-brain entrainment: EEG interbrain synchronization while speaking and listening. Scientific reports, 7(1), pp.1-12.
There is another one in which the brains of couples; boyfriends and girlfriends, husbands and wives, synchronized far more than those of strangers (who were only introduced after agreeing to participate in the experiment) in ordinary conversations. If they were romantically and/or sexually involved, or had lifetime partnerships, their brains synchronized with each other when they were talking together, but not if they had just met.
Kinreich, S., Djalovski, A., Kraus, L., Louzoun, Y. and Feldman, R., 2017. Brain-to-brain synchrony during naturalistic social interactions. Scientific reports, 7(1), pp.1-12.
Another study found that there was more synchronization between the brains of mothers and children when the kids and their mothers took turns speaking, so that one talked while the other was listened, and vice versa.
Nguyen, T., Schleihauf, H., Kayhan, E., Matthes, D., Vrtička, P. and Hoehl, S., 2021. Neural synchrony in mother–child conversation: Exploring the role of conversation patterns. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 16(1-2), pp.93-102.
This is hard to explain in terms of mirror neuron activity because listening and speaking are very different as far as the brain is concerned. To give one example, a listener does not sympathize with the person telling a story, they sympathize with the people in the story or they focus on its events. That’s very different from focusing on the one speaking, and mirror neurons act primarily to allow us to identify with other people’s current actions. They ‘mirror’ the actions of other people, and listening doesn’t mirror talking.
There is another study that explains how direct eye contact between mothers and children increases their “neural coupling”.
Leong, V., Byrne, E., Clackson, K., Georgieva, S., Lam, S. and Wass, S., 2017. Speaker gaze increases information coupling between infant and adult brains. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(50), pp.13290-13295.
A further experiment, involving mothers and children, showed that there was increased synchronization in the gamma range, when mothers and children watched videos of themselves interacting. Interestingly, it only appeared when they were watching videos of positive interactions. It didn’t appear when the mothers and infants were watching videos of themselves in a conflict, or when they were watching videos of other mothers with their children.
Levy, J., Goldstein, A. and Feldman, R., 2017. Perception of social synchrony induces mother–child gamma coupling in the social brain. Social cognitive and affective neuroscience, 12(7), pp.1036-1046.
This kind of interaction increases human bonding, and we can probably infer that it also decreases human conflict.
Brain-to-brain information sharing isn’t limited to human beings; it appears to happen for many social species, including mice and bats.
One study showed that frontal lobe activity in of pairs mice became more correlated with one another when two of the mice were relating to each other, but not when they weren’t.
Kingsbury, L., Huang, S., Wang, J., Gu, K., Golshani, P., Wu, Y.E. and Hong, W., 2019. Correlated neural activity and encoding of behavior across brains of socially interacting animals. Cell, 178(2), pp.429-446.
We see almost the same result with bats. Neural activity in pairs of bats correlated when they were interacting socially.
Zhang, W. and Yartsev, M.M., 2019. Correlated neural activity across the brains of socially interacting bats. Cell, 178(2), pp.413-428.
It’s interesting to see it in more than one species, and we can expect to see more results like this in time, with the strongest animal correlations appearing in social species, where relating to others is a crucial skill.
Let me try to give you a brief summary (repeated from the summary at the beginning of this article), and to offer a conclusion.
Chi looks like it’s a magnetic phenomenon.
Chi (“Qi” or “Ki” in Japanese, as in “Aikido” or “Reiki”) is the “subtle energy” or “life force” that’s the foundation for acupuncture, some martial arts, and traditional Asian healing “by laying on hands”. In Chinese tradition, Chi doesn’t have a physical basis. However, there is evidence that suggests it may be a magnetic phenomenon. Whether it’s physical or not depends on your definition for the word ‘matter’.
Chi or Reiki practice can create magnetic fields in the practitioner’s hands, and magnetic fields can pass information between brains. Reiki also appears to synchronize some of the activity between the brains of the practitioner and the brains of their clients.
Spiritual healing may work by passing information from the healer’s brain to the client’s brain through magnetism that runs through the healer’s hands, recruiting local neurons in the area where the area where they apply them. brain-to-brain communication also happens directly between brains in other contexts.
Whether it’s called “healing by laying on hands”, “spiritual healing”, “energy healing”, “Qigong” or even “quantum healing” (a misnomer). This ancient technique is found everywhere in the world, and seen throughout history.
However, healing hands may actually be healing brains, and the healing force may be the force of magnetism, carrying the message from the healer’s brain to the patient’s brain and from there to their body: “be thou healed and made whole.”
End.
References:
“Detection of extraordinary large bio-magnetic field strength from human hand during external Qi emission”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1353653/
“Practicing Reiki does not appear to routinely produce high-intensity electromagnetic fields from the heart or hands of Reiki practitioners.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23210468/
Magnetite biomineralization in the human brain.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1502184/
“Enhanced coherence within the theta band between pairs of brains engaging in experienced versus naïve Reiki procedures.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24967637/
“Brain-to-brain communication: the possible role of brain electromagnetic fields (As a Potential Hypothesis).”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33732922/
“Investigating Cooperative Behavior in Ecological Settings: An EEG Hyperscanning Study.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27124558/
“Brain-to-brain coupling during handholding is associated with pain reduction.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29483250/
“Speaker gaze increases information coupling between infant and adult brains.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29183980/
“Intra- and interbrain synchronization and network properties when playing guitar in duets.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23226120/
“Physical presence of spouse enhances brain-to-brain synchrony in co-parenting couples.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32371912/
“How Two Brains Make One Synchronized Mind in the Inferior Frontal Cortex: fNIRS-Based Hyperscanning During Cooperative Singing.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26635703/
“Brain-to-brain entrainment: EEG interbrain synchronization while speaking and listening.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28646190/
“Brain-to-Brain Synchrony during Naturalistic Social Interactions.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29213107/
“Suffer together, bond together: Brain-to-brain synchronization and mutual affective empathy when sharing painful experiences.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34116146/
“Perception of social synchrony induces mother-child gamma coupling in the social brain.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28402479/
“Correlated Neural Activity and Encoding of Behavior across Brains of Socially Interacting Animals.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31230711/
“Correlated Neural Activity across the Brains of Socially Interacting Bats.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31230710/
Other Pages On This Site:
NEURAL STIMULATION:
The God Helmet | Shiva Psychic Technology
Shakti – Magnetic Brain Stimulation
Inventing Shakti
Stimulating My Brain As A Spiritual Path
HUMAN EVOLUTION:
Origins of spirituality in Human Evolution
Role of Mystics and mysticism in Human Evolution.
The Gay Male Brain in human evolution
The Evolution of Human Belief in God
Consciousness | Darwinian Reincarnation
SPIRITUAL
NEUROSCIENCE
Articles on neurotheology, (or – spirituality and religion meet brain science).
Enlightenment And the Brain
Deja Vu | Meditations from Brain Science
Romantic Love and the Brain
The Sensed Presence | God in the Brain
Spiritual Aptitude Test | Sacred Lands
The Spiritual Personality | Archetypes
Out-Of-Body Experiences | Visions
Odd Experiences – Online Poll Results
Podcasts on Neurotheology
OFF-SITE PAGES (OPEN IN NEW WINDOWS).
Different spiritual practices have different effects on the brain.
NEAR-DEATH EXPERIENCES:
NDEs in Thailand – Discussion | Thai NDE Case histories
Darwinian Reincarnation
Near-Death Experience Screensaver (Entering the Light).
Epilepsy And Near-Death Experiences
BRAIN STUFF:
Glasses For Enhanced Visual Acuity
A Diet For Epileptics?
Sex & States of Consciousness
Hippocrates on Epilepsy
The Terrorist Brain
OTHER STUFF: